Disease background
Types of cystinosis
There are three clinically recognised forms of cystinosis, depending on the age of presentation and degree of renal disease severity:1,2
Infantile nephropathic cystinosis
The most severe and frequent form, accounting for 95% of patients1,2
The major identifiable cause of renal Fanconi syndrome in children1,2
If untreated, leads to end-stage renal disease in the first decade of life1,2
Juvenile, or late-onset, nephropathic cystinosis
Accounts for 5% of patients1,2
Usually diagnosed later in childhood or during adolescence2
Symptoms are often more unspecific and incomplete compared with the infantile form, e.g. nephrotic syndrome or mild proximal tubulopathy2
Slower progression to end-stage renal disease1
Adult, or ocular, cystinosis
Rarely diagnosed before adulthood1,2
Characterised by photophobia due to corneal cystine accumulation1,2
Kidneys may still be affected1,2
Pathophysiology
Nephropathic cystinosis occurs as a result of mutations in the gene CTNS, which codes for the lysosomal cystine-proton cotransporter cystinosin. To date, more than 160 pathogenic variants have been identified in the CTNS gene.1-3
Cystinosin is ubiquitously expressed on lysosomal membranes; when the protein is functional, cystine efflux from the lysosome is driven by a proton gradient. However, in the absence of a functional transporter, cystine accumulates and crystallises inside the lysosome.1,4
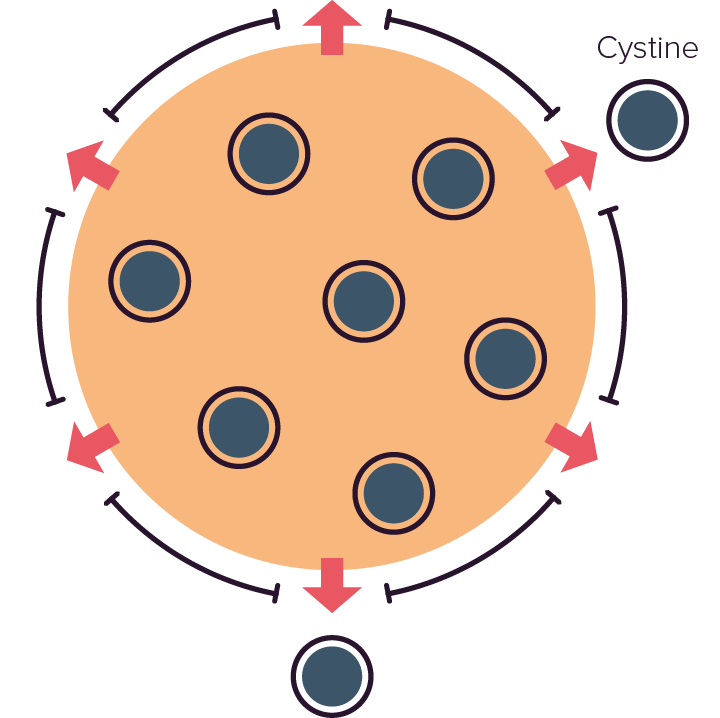
Normal lysosome

Lysosome in nephropathic cystinosis
Cystine crystals have a number of pathological effects, such as:1,2
Activation of monocytes and macrophages, which leads to the production of pro-inflammatory substances
Enhanced apoptosis
Increased oxidative stress
More recent research has also demonstrated that cystinosin plays a broader role in intracellular vesicle trafficking, cell signalling, lysosomal dynamics and exocytosis, all of which may be disrupted by cystinosin dysfunction.5
To date, the exact mechanisms behind the clinical symptoms of the disease are not fully understood and may differ between tissues.2,5
Explore the sections below to find out more
Disease background
Types of cystinosis and pathophysiology of nephropathic cystinosis




